What is OT Security? A Complete Guide to Operational Technology

Operational Technology (OT) security is a crucial aspect of modern industry, focusing on protecting systems that control and monitor physical devices, processes, and infrastructure. As technology advances, the lines between IT and OT continue to blur, making OT security more important than ever. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of OT security, exploring its definition, key components, and best practices for securing these critical systems. By understanding OT security, organizations can safeguard their operational integrity, prevent downtime, and protect against ever-evolving cyber threats that target industrial control systems and critical infrastructure. Effective OT security is essential.
Understanding OT Security: A Comprehensive Overview
Operational Technology (OT) security refers to the protection of systems, networks, and devices used to monitor, control, and manage industrial operations. This includes Industrial Control Systems (ICS), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and other connected devices. OT security is critical in preventing cyber threats and physical harm to people, the environment, and the economy.
What is Operational Technology (OT)?
Operational Technology (OT) encompasses a range of technologies used to manage and control industrial operations, including manufacturing, transportation, energy, and water systems. OT systems are designed to monitor, control, and optimize industrial processes, and are typically used in real-time environments. The primary goal of OT is to ensure the safe and efficient operation of industrial processes.
The Importance of OT Security
OT security is essential in preventing cyber attacks that could compromise the integrity and availability of OT systems. A cyber breach could result in physical harm to people, environmental damage, and economic loss. OT security measures help to protect OT systems from malicious actors and unauthorized access. This includes implementing security protocols, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Types of OT Security Threats
There are several types of OT security threats, including malware, phishing, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Malware can compromise OT systems, while phishing attacks can trick operators into revealing sensitive information. DoS attacks can overwhelm OT systems, rendering them unavailable. Other threats include insider threats, physical threats, and supply chain threats.
OT Security Measures and Controls
To mitigate OT security threats, organizations can implement various security measures and controls. This includes network segmentation, access control, and incident response planning. Network segmentation helps to isolate OT systems from other networks, while access control restricts access to authorized personnel. Incident response planning ensures that organizations are prepared to respond to security incidents.
Benefits of Implementing OT Security
Implementing OT security measures can provide several benefits, including improved security, reduced risk, and increased efficiency. Improved security helps to prevent cyber attacks and physical harm, while reduced risk minimizes the likelihood of security incidents. Increased efficiency can result from optimized OT systems and improved incident response.
| OT Security Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Network Segmentation | Improved Security, Reduced Risk |
| Access Control | Improved Security, Increased Efficiency |
| Incident Response Planning | Reduced Risk, Increased Efficiency |
| Firewalls | Improved Security, Reduced Risk |
| Intrusion Detection Systems | Improved Security, Increased Efficiency |
What is operational technology (OT) security?

Operational technology (OT) security refers to the protection of hardware and software systems used to monitor, control, and manage industrial operations, such as those found in power plants, water treatment facilities, and transportation systems. OT security is critical because these systems are often interconnected and can have a significant impact on public safety and economic stability if compromised. The primary goal of OT security is to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks that could disrupt or manipulate industrial operations.
Importance of OT Security
The importance of OT security cannot be overstated, as a cyber attack on an industrial control system could have catastrophic consequences. Some of the key reasons why OT security is essential include:
- Protection of critical infrastructure from cyber threats and physical harm
- Prevention of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information
- Maintenance of system integrity and reliability to ensure continuous operation
Effective OT security measures can help prevent disruptions to industrial operations, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Challenges in OT Security
OT security faces several challenges, including the use of legacy systems, limited resources, and complexity of industrial operations. Some of the key challenges in OT security include:
- Inadequate security protocols and outdated software that can leave systems vulnerable to cyber attacks
- Insufficient training and lack of awareness among operators and maintenance personnel
- Difficulty in implementing security patches and updates without disrupting industrial operations
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to OT security that includes risk assessment, vulnerability management, and incident response planning.
Best Practices for OT Security
To ensure the security of OT systems, organizations should follow best practices that include regular maintenance, security assessments, and incident response planning. Some of the key best practices for OT security include:
- Implementing strong access controls and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access
- Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities
- Developing an incident response plan to quickly respond to cyber attacks and minimize downtime
By following these best practices, organizations can help protect their OT systems from cyber threats and ensure the reliability and integrity of industrial operations.
What is the salary of OT security?
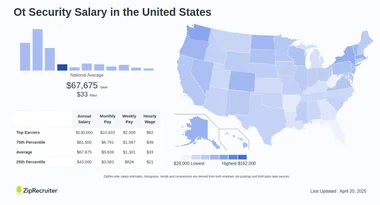
The salary of OT security can vary depending on factors such as location, industry, level of experience, and specific job requirements. However, the average salary range for OT security professionals is between $80,000 to over $200,000 per year. Cybersecurity experts with experience in OT security can earn higher salaries due to the high demand for their skills.
Factors Affecting OT Security Salary
The salary of OT security professionals is influenced by several factors, including location, industry, and level of experience. Some of the key factors affecting OT security salary are:
- Geographic location: Salaries can vary significantly depending on the location, with cities like San Francisco and New York tend to offer higher salaries than other parts of the country.
- Industry: OT security professionals working in critical infrastructure industries such as energy, transportation, and healthcare tend to earn higher salaries due to the high stakes involved.
- Level of experience: More experienced OT security professionals can earn higher salaries, with senior roles often commanding salaries over $150,000 per year.
OT Security Job Roles and Salaries
OT security professionals can work in a variety of job roles, each with its own salary range. Some of the common OT security job roles and their average salary ranges are:
- OT Security Engineer: $90,000 - $140,000 per year, responsible for designing and implementing secure systems and networks.
- OT Security Consultant: $100,000 - $160,000 per year, providing expert advice on OT security to organizations.
- OT Security Manager: $120,000 - $200,000 per year, overseeing OT security teams and developing security strategies.
Skills and Certifications for OT Security Professionals
OT security professionals require a range of technical skills and certifications to be successful in their roles. Some of the key skills and certifications for OT security professionals include:
- Knowledge of OT protocols: Such as Modbus and ICS protocols.
- Experience with security technologies: Such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Certifications: Such as CISSP and CEH, which demonstrate expertise in cybersecurity and OT security.
What are the key components of OT security?
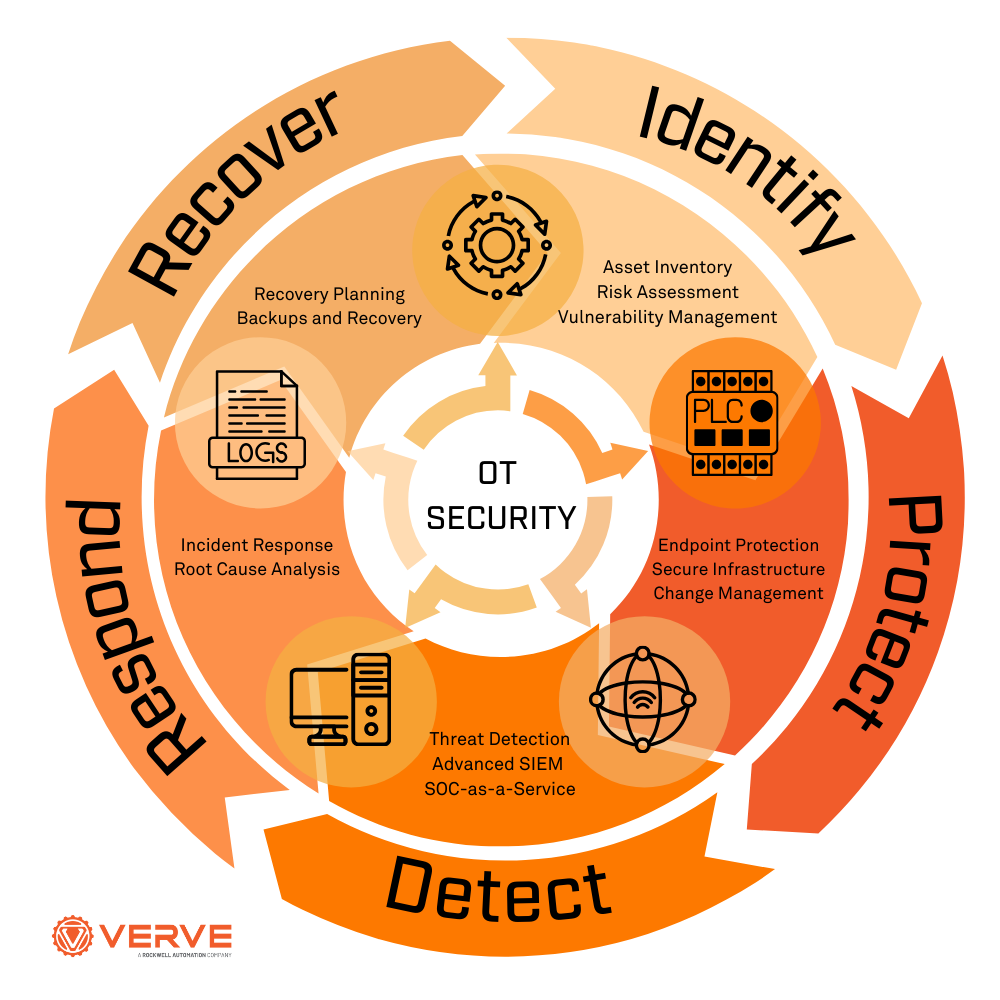
The key components of Operational Technology (OT) security are designed to protect the control systems and devices that manage and monitor industrial processes. These components work together to prevent cyber threats and ensure the reliability and safety of OT systems.
Network Segmentation and Isolation
Network segmentation and isolation are critical components of OT security, as they help to limit the attack surface and prevent lateral movement in case of a security breach. This can be achieved through the use of firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and access control lists (ACLs). Some key considerations for network segmentation and isolation include:
- Implementing segmentation to isolate critical systems and devices from the rest of the network
- Using firewalls to control traffic flow and block unauthorized access
- Configuring VPNs to encrypt and protect remote access to OT systems
Device Hardening and Patch Management
Device hardening and patch management are essential components of OT security, as they help to reduce vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation by attackers. This can be achieved through the use of secure configuration and patch management practices. Some key considerations for device hardening and patch management include:
- Implementing secure configuration to disable unnecessary services and features
- Using patch management to keep software up-to-date and patch vulnerabilities
- Conducting regular vulnerability assessments to identify and remediate potential security risks
Monitoring and Incident Response
Monitoring and incident response are critical components of OT security, as they help to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely and effective manner. This can be achieved through the use of security information and event management (SIEM) systems and incident response plans. Some key considerations for monitoring and incident response include:
- Implementing SIEM systems to monitor and analyze security-related data
- Developing incident response plans to respond to and contain security incidents
- Conducting regular training and exercises to ensure preparedness and response effectiveness
What is an example of OT security?

An example of OT security is the protection of Industrial Control Systems (ICS), which are used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as power generation and distribution, water treatment, and transportation systems. OT security involves the implementation of security measures to prevent unauthorized access, damage, or disruption to these systems, which could have serious consequences for public health and safety, as well as the economy.
OT Security in Industrial Environments
OT security in industrial environments is critical to prevent cyber attacks on SCADA systems, which are used to monitor and control industrial processes. This can be achieved through the implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, such as authentication and authorization. Some key measures to ensure OT security in industrial environments include:
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities
- Implementing security protocols to prevent unauthorized access to ICS systems
- Providing training to personnel on OT security best practices and incident response
OT Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
OT security threats and vulnerabilities are numerous and can have serious consequences if not addressed. Some common threats include malware, phishing, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, which can compromise the availability and integrity of OT systems. To mitigate these threats, it is essential to implement security controls, such as patch management, vulnerability assessment, and penetration testing. Some key vulnerabilities to address include:
- Unpatched software and outdated systems that can be exploited by attackers
- Weak passwords and insufficient authentication mechanisms
- Lack of segmentation and isolation of OT systems from the internet and other networks
Best Practices for OT Security
Best practices for OT security involve a combination of technical, operational, and managerial measures to prevent and respond to cyber threats. Some key best practices include implementing defense-in-depth strategies, which involve multiple layers of security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. Additionally, incident response planning and continuity planning are essential to ensure that OT systems can be quickly restored in the event of a cyber attack or other disruption. Some key best practices to follow include:
- Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) systems to monitor and analyze security logs
- Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities
- Developing and implementing incident response plans and continuity plans to ensure business continuity
Frequently Asked Questions
What is OT Security and How Does it Differ from IT Security?
OT security, also known as Operational Technology security, refers to the protection of systems, networks, and devices that are used to monitor, control, and manage industrial operations, such as power plants, transportation systems, and manufacturing facilities. Unlike IT security, which focuses on protecting data and information systems, OT security is concerned with ensuring the reliability, safety, and efficiency of industrial processes. This requires a different approach to security, as OT systems often have unique characteristics, such as real-time operation and physical interactions, that are not typically found in IT systems. As a result, OT security requires a deep understanding of industrial control systems, SCADA systems, and other operational technologies.
What are the Key Components of an OT Security Solution?
A comprehensive OT security solution typically includes several key components, such as network segmentation, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to prevent unauthorized access and malicious activity. Additionally, OT security solutions often involve vulnerability management, patch management, and configuration management to ensure that systems and devices are up-to-date and securely configured. Encryption and authentication mechanisms are also essential to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Furthermore, OT security solutions must be able to monitor and analyze system activity in real-time, to quickly detect and respond to potential security threats. By combining these components, organizations can create a robust OT security solution that protects their industrial operations and ensures business continuity.
What are the Most Common OT Security Threats and How Can They be Mitigated?
OT systems are vulnerable to a range of security threats, including cyber attacks, physical attacks, and insider threats. Some of the most common OT security threats include ransomware, malware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, which can cause system downtime, data loss, and physical harm. To mitigate these threats, organizations can implement security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, to prevent unauthorized access and malicious activity. Additionally, regular security audits and risk assessments can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in OT systems, allowing organizations to take proactive steps to mitigate and remediate potential threats. By combining these measures, organizations can reduce the risk of OT security breaches and ensure the reliability and safety of their industrial operations.
How Can Organizations Implement an Effective OT Security Strategy?
Implementing an effective OT security strategy requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the unique characteristics and requirements of OT systems. This includes conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses, as well as developing a tailored security plan that addresses the specific needs of the organization. Additionally, training and awareness programs can help personnel understand the importance of OT security and their role in maintaining and enhancing the security of OT systems. Furthermore, regular security testing and evaluation can help ensure that OT security measures are effective and up-to-date, and that the organization is prepared to respond to potential security incidents. By taking a proactive and comprehensive approach to OT security, organizations can protect their industrial operations, ensure business continuity, and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
Leave a Reply