How to Secure Operational Technology (OT) in Critical Infrastructure
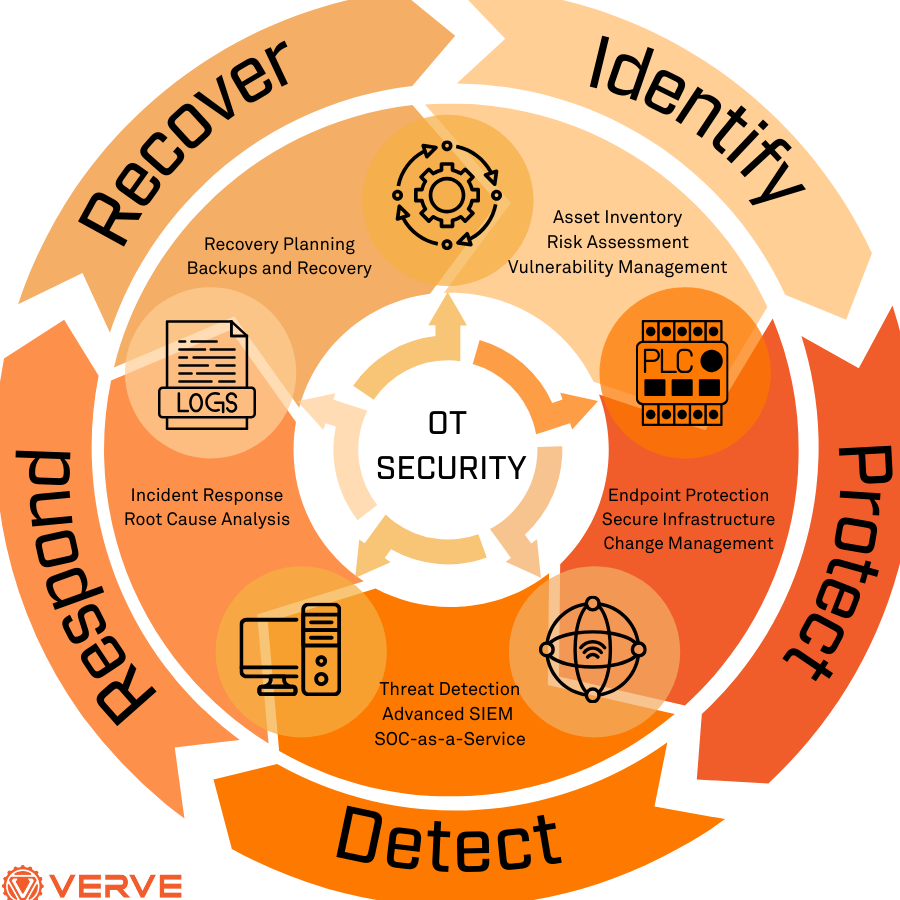
Operational Technology (OT) is crucial in critical infrastructure, controlling and monitoring essential systems. As OT systems become increasingly interconnected, they are exposed to growing cyber threats. Securing OT is vital to prevent disruptions, ensure public safety, and protect national security. Effective OT security requires a comprehensive approach, including risk assessments, vulnerability management, and incident response planning. This article will provide guidance on how to secure OT in critical infrastructure, protecting against cyber threats and ensuring the reliability and resilience of these essential systems. Implementing robust security measures is essential to safeguard OT systems.
Understanding the Importance of Securing Operational Technology (OT) in Critical Infrastructure
Securing Operational Technology (OT) in critical infrastructure is crucial for the protection of national security, public health, and safety. OT refers to the hardware and software used to control and monitor industrial processes, such as those found in power plants, water treatment facilities, and transportation systems. The security of OT systems is essential to prevent cyber threats, physical harm, and economic disruption. In recent years, there has been an increase in cyber attacks on OT systems, highlighting the need for robust security measures to be implemented.
Assessing the Risks to Operational Technology (OT) Systems
Assessing the risks to OT systems is the first step in securing them. This involves identifying potential vulnerabilities and threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. It is also important to consider the potential consequences of a cyber attack, including loss of life, environmental damage, and economic disruption. By understanding the risks, organizations can develop effective security strategies to mitigate them.
Implementing Secure Architecture and Design
Implementing secure architecture and design is critical to securing OT systems. This involves designing systems with security in mind, using secure protocols, and implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems. It is also important to consider the supply chain risk, ensuring that all components and software used in OT systems are secure and trusted. By implementing secure architecture and design, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and malicious activity.
Conducting Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing is essential to identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in OT systems. These tests involve simulating cyber attacks to identify potential entry points and weaknesses, allowing organizations to remediate them before they can be exploited. By conducting regular security audits and penetration testing, organizations can ensure that their OT systems are secure and resilient.
Developing Incident Response Plans
Developing incident response plans is critical to responding to cyber attacks on OT systems. These plans involve identifying incident response teams, communication protocols, and mitigation strategies. By having a plan in place, organizations can quickly respond to cyber incidents, minimizing damage and downtime. It is also important to regularly test and update incident response plans to ensure they are effective and relevant.
Training and Awareness for Operational Technology (OT) Security
Training and awareness are essential for OT security. This involves educating personnel on security best practices, cyber threats, and incident response procedures. By providing regular training and awareness programs, organizations can ensure that their personnel are equipped to respond to cyber incidents and prevent security breaches. It is also important to consider the human factor, ensuring that personnel understand the importance of security and their role in protecting OT systems.
| Security Measure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Firewalls | Network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic | Prevents unauthorized access, blocks malicious traffic |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | System that monitors network traffic for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activity | Detects and alerts on potential security threats, provides real-time monitoring |
| Encryption | Process of converting plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext | Protects data in transit and at rest, ensures confidentiality and integrity |
| Secure Protocols | Communication protocols that provide secure data transfer, such as HTTPS and SFTP | Ensures secure data transfer, prevents eavesdropping and tampering |
| Regular Security Audits | Process of identifying and remediating vulnerabilities and weaknesses in OT systems | Identifies and remediates security vulnerabilities, ensures compliance with regulations |
How to secure operational technology?

Securing operational technology is crucial to prevent cyber attacks and protect critical infrastructure. Operational technology refers to the hardware and software used to control and monitor industrial processes, such as power grids, water treatment plants, and transportation systems. To secure operational technology, it is essential to implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and malicious activities.
Implementing Secure Network Architecture
Implementing a secure network architecture is vital to protect operational technology from cyber threats. This can be achieved by segmenting the network into isolated zones, each with its own security controls and access restrictions. Additionally, firewalls and intrusion detection systems can be used to monitor and block suspicious traffic. Some key steps to implement a secure network architecture include:
- Conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities
- Implementing network segmentation to isolate critical systems
- Using encryption to protect data in transit and at rest
Conducting Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments
Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments is essential to identify and mitigate potential security threats to operational technology. These audits should include vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and compliance checks to ensure that the system is secure and compliant with industry regulations. Some key steps to conduct regular security audits and risk assessments include:
- Identifying and prioritizing high-risk assets and systems
- Conducting regular vulnerability assessments to identify potential weaknesses
- Implementing remediation plans to address identified vulnerabilities
Training and Awareness for Operational Technology Security
Providing training and awareness to personnel is crucial to ensure the security of operational technology. This includes security awareness training to educate personnel on security best practices and phishing attacks, as well as technical training to ensure that personnel have the necessary skills and knowledge to operate and maintain secure systems. Some key steps to provide training and awareness for operational technology security include:
- Developing a comprehensive security awareness program to educate personnel
- Providing regular training on security best practices and industry regulations
- Encouraging a culture of security within the organization to promote security awareness and responsibility
What is operational technology (OT) security?

Operational technology (OT) security refers to the protection of hardware and software systems used to monitor, control, and manage industrial operations, such as those found in power plants, water treatment facilities, and transportation systems. OT security is critical to preventing cyber attacks that could compromise the safety and reliability of these systems, as well as the environment and public health.
What are the Key Components of OT Security?
The key components of OT security include network segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control. These components work together to prevent unauthorized access to OT systems and protect against malware and other types of cyber threats. Some of the key features of OT security include:
- Real-time monitoring of OT systems to detect potential security threats
- Incident response planning to quickly respond to security incidents
- Regular security updates and patching to prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities
What are the Benefits of Implementing OT Security?
Implementing OT security can provide several benefits, including improved safety, reduced downtime, and increased efficiency. By protecting OT systems from cyber threats, organizations can prevent disruptions to operations and minimize the risk of accidents. Some of the benefits of OT security include:
- Enhanced cybersecurity posture to protect against evolving threats
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards
- Reduced risk of data breaches and other security incidents
What are the Challenges of Implementing OT Security?
Implementing OT security can be challenging due to the complexity of OT systems and the limited resources available to support security efforts. Additionally, OT systems often have unique security requirements that must be addressed, such as the need for real-time monitoring and low latency. Some of the challenges of implementing OT security include:
- Integrating OT security with existing IT security systems to provide comprehensive protection
- Addressing the skills gap in OT security to ensure that personnel have the necessary expertise
- Managing the cost of OT security to ensure that it is effective and affordable
What is OT in critical infrastructure?
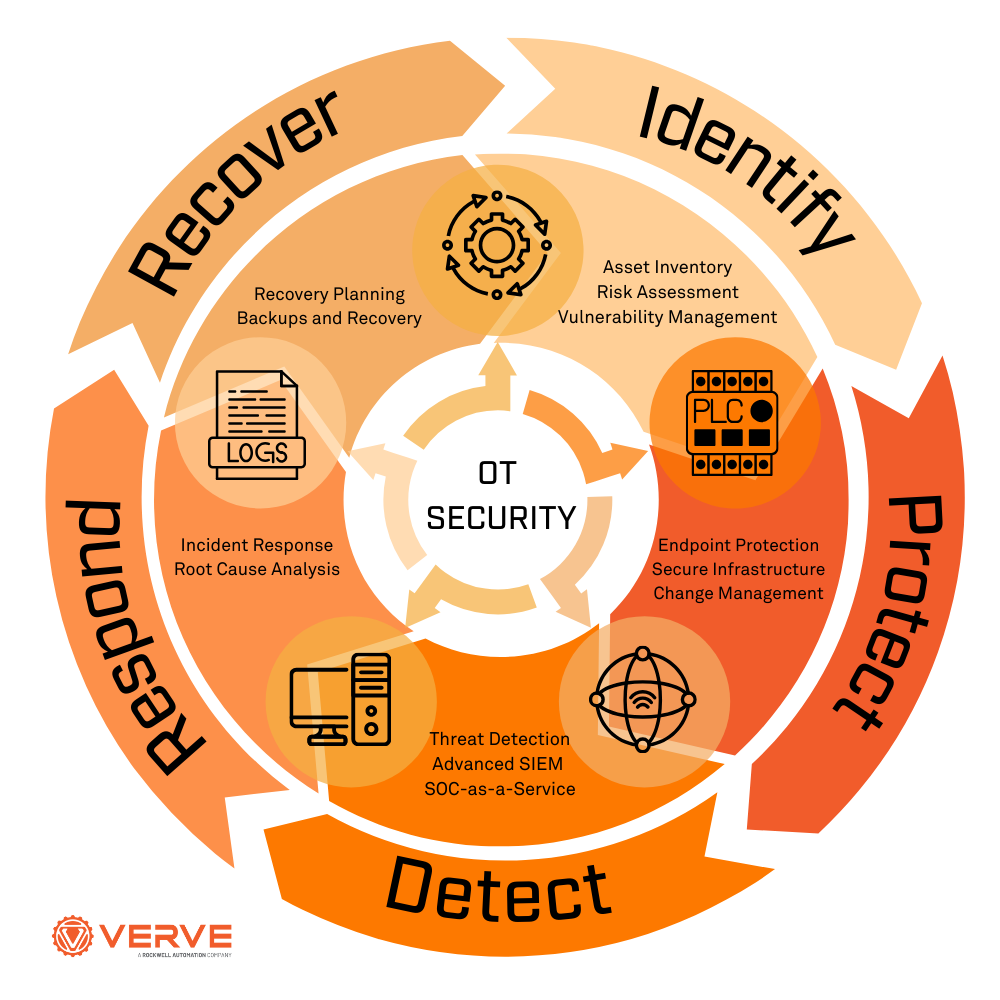
OT in critical infrastructure refers to Operational Technology, which encompasses the hardware and software systems used to monitor, control, and manage the operational processes of critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, transportation, water, and healthcare. These systems are designed to ensure the reliable and efficient operation of critical infrastructure, and their failure can have significant consequences for public health, safety, and economic stability.
Overview of OT in Critical Infrastructure
The use of OT in critical infrastructure is pervasive, with applications in power generation and distribution, water treatment and distribution, transportation systems, and healthcare facilities. OT systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes, supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, and distributed control systems (DCS). Some key features of OT in critical infrastructure include:
- Real-time monitoring and control of operational processes
- Automated decision-making and control systems
- Integration with other systems, such as information technology (IT) systems and internet of things (IoT) devices
Security Risks and Challenges in OT
The increasing interconnectedness of OT systems with IT systems and IoT devices has introduced new security risks and challenges. OT systems are often vulnerable to cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Some key security risks and challenges in OT include:
- Lack of visibility into OT system networks and assets
- Inadequate security controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Insufficient training and awareness of OT system security risks and best practices
Best Practices for OT Security in Critical Infrastructure
To address the security risks and challenges associated with OT in critical infrastructure, organizations should implement best practices such as network segmentation, access control, and continuous monitoring. Some key best practices for OT security include:
- Conducting regular risk assessments and vulnerability scans
- Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) systems
- Developing and enforcing incident response plans and security policies
What are the examples of OT security?

The examples of OT security include various measures to protect operational technology systems from cyber threats. OT security is crucial in industries such as energy, transportation, and manufacturing, where industrial control systems are used to monitor and control physical processes.
OT Security Measures
OT security measures include implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access to OT networks. Additionally, encryption and secure communication protocols are used to protect data transmitted between OT devices. Some examples of OT security measures include:
- Implementing access control measures, such as role-based access control and multi-factor authentication, to restrict access to OT systems
- Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks
- Developing incident response plans to quickly respond to and contain security incidents
OT Security Threats
OT security threats include various types of malware, such as ransomware and Trojans, that can compromise OT systems and disrupt physical processes. Other threats include denial-of-service attacks, which can overwhelm OT systems with traffic, and insider threats, which can come from authorized personnel with malicious intentions. Some examples of OT security threats include:
- Phishing attacks, which can trick authorized personnel into divulging sensitive information or clicking on malicious links
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities, which can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to OT systems
- Physical attacks, which can involve tampering with OT devices or disrupting physical processes
OT Security Best Practices
OT security best practices include implementing security-by-design principles, which involve designing OT systems with security in mind from the outset. Additionally, security awareness training is essential to educate authorized personnel on security best practices and the importance of information security. Some examples of OT security best practices include:
- Implementing change management processes to ensure that changes to OT systems are carefully planned and tested
- Using secure protocols for communication between OT devices, such as secure socket layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS)
- Conducting regular security testing and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and improve OT security
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Operational Technology (OT) and Why is it Important to Secure it in Critical Infrastructure?
Operational Technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software systems used to manage and control industrial processes in critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, water, transportation, and manufacturing. Securing OT is crucial because it plays a vital role in maintaining the reliability, safety, and efficiency of these systems. A cyber attack on OT systems can have catastrophic consequences, including disruption of essential services, economic losses, and even loss of life. Therefore, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect OT systems from cyber threats and ensure the continuity of operations in critical infrastructure.
What are the Common Cyber Threats to Operational Technology (OT) in Critical Infrastructure?
The common cyber threats to Operational Technology (OT) in critical infrastructure include malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. These threats can be intentional or unintentional, and can originate from insiders or outsiders. Insider threats can come from employees or contractors with authorized access to OT systems, while outsider threats can come from hackers, nation-state actors, or terrorist organizations. Additionally, OT systems are often connected to the internet, which increases their vulnerability to cyber attacks. Therefore, it is essential to implement robust security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, to prevent or detect these threats.
How Can Organizations Implement Effective Security Measures to Protect Operational Technology (OT) in Critical Infrastructure?
To implement effective security measures to protect Operational Technology (OT) in critical infrastructure, organizations should adopt a defense-in-depth approach that includes multiple layers of security controls. This can include network segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, access controls, and encryption. Organizations should also implement regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and remediate security weaknesses. Additionally, employee training and awareness programs are essential to prevent insider threats and ensure that employees understand the importance of cybersecurity. Furthermore, organizations should develop incident response plans to quickly respond to cyber attacks and minimize their impact.
What are the Best Practices for Ensuring the Cybersecurity of Operational Technology (OT) in Critical Infrastructure?
The best practices for ensuring the cybersecurity of Operational Technology (OT) in critical infrastructure include implementing a robust cybersecurity framework, conducting regular security risk assessments, and developing incident response plans. Organizations should also implement secure remote access controls, use secure communication protocols, and monitor OT systems for anomalies and suspicious activity. Additionally, collaboration and information sharing between organizations and government agencies are essential to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices. Furthermore, organizations should invest in cybersecurity research and development to stay ahead of emerging threats and develop new security technologies to protect OT systems in critical infrastructure.
Leave a Reply