Understanding OT SCADA Security: Challenges and Solutions

The increasing reliance on Operational Technology (OT) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems in critical infrastructure has created new cybersecurity challenges. As these systems control and monitor essential services, their security is paramount. However, the unique characteristics of OT and SCADA systems, such as legacy equipment and limited resources, make securing them a complex task. This article will explore the challenges and solutions to understanding OT SCADA security, providing insights into the current landscape and best practices for protecting these critical systems from emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Effective security measures are crucial.
Understanding OT SCADA Security: Challenges and Solutions
The security of Operational Technology (OT) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems is a critical concern for organizations that rely on these systems to manage and control their operations. OT SCADA security refers to the protection of these systems from cyber threats and attacks that could compromise their integrity, availability, and confidentiality. The goal of OT SCADA security is to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of these systems and their components.
Introduction to OT SCADA Systems
OT SCADA systems are used to monitor, control, and manage industrial processes, such as power generation and transmission, water treatment, transportation, and manufacturing. These systems typically consist of sensors, actuators, control systems, and communication networks that work together to collect data, make decisions, and take actions. The security of OT SCADA systems is critical because they often control physical processes that can have a significant impact on the environment, public health, and safety.
Cyber Threats to OT SCADA Systems
OT SCADA systems are vulnerable to various types of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. These threats can be launched by hackers, terrorists, or nation-states seeking to disrupt or exploit these systems for their own gain. The consequences of a successful cyber attack on an OT SCADA system can be severe, including equipment damage, production downtime, financial losses, and environmental harm.
Challenges in Securing OT SCADA Systems
Securing OT SCADA systems poses several challenges, including the use of legacy systems, lack of standardization, insufficient security controls, and limited resources. Additionally, OT SCADA systems often have complex architectures and interdependencies that make it difficult to identify and mitigate potential security risks. Furthermore, the convergence of IT and OT has introduced new security risks and challenges, such as the need to integrate IT security controls with OT security controls.
Solutions for Securing OT SCADA Systems
To address the challenges and threats associated with OT SCADA systems, organizations can implement various security solutions, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), incident response plans, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. Additionally, organizations can adopt best practices, such as regular security assessments, penetration testing, and security awareness training, to help protect their OT SCADA systems from cyber threats.
Benefits of Implementing OT SCADA Security Measures
Implementing OT SCADA security measures can provide several benefits, including improved security posture, reduced risk, increased compliance, and enhanced reputation. By protecting their OT SCADA systems from cyber threats, organizations can also prevent financial losses, minimize downtime, and ensure business continuity. The following table summarizes some of the key benefits of implementing OT SCADA security measures:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Security Posture | Reduced vulnerability to cyber threats and attacks |
| Reduced Risk | Minimized risk of equipment damage, production downtime, and financial losses |
| Increased Compliance | Adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards |
| Enhanced Reputation | Protection of brand image and reputation through effective security measures |
| Prevention of Financial Losses | Avoidance of costs associated with cyber attacks and system downtime |
The implementation of OT SCADA security measures requires a comprehensive approach that includes risk assessment, vulnerability management, incident response, and security awareness training. By taking a proactive approach to OT SCADA security, organizations can help protect their systems and prevent cyber attacks.
What are the security issues with SCADA?
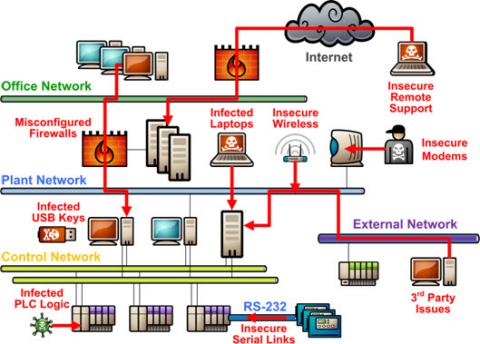
The security issues with SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are a major concern as they can have a significant impact on the reliability and safety of critical infrastructure. SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as power generation and transmission, water treatment, and transportation systems. However, these systems are often vulnerable to cyber threats, which can compromise their integrity and availability.
Network Security Risks
The network security risks associated with SCADA systems are a major concern. These systems often rely on legacy protocols and outdated software, which can make them susceptible to hacking and other cyber attacks. Some of the key network security risks associated with SCADA systems include:
- Unauthorized access to the system, which can allow hackers to manipulate the system and disrupt operations
- Malware attacks, which can compromise the integrity of the system and steal sensitive data
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can overwhelm the system and make it unavailable to authorized users
System Vulnerabilities
The system vulnerabilities associated with SCADA systems are another major concern. These systems often have complex architectures and interdependent components, which can make them difficult to secure. Some of the key system vulnerabilities associated with SCADA systems include:
- Buffer overflow vulnerabilities, which can allow hackers to execute malicious code and gain unauthorized access to the system
- SQL injection vulnerabilities, which can allow hackers to manipulate the system's database and steal sensitive data
- Privilege escalation vulnerabilities, which can allow hackers to elevate their privileges and gain unauthorized access to sensitive areas of the system
Human Factors
The human factors associated with SCADA systems are also a major concern. These systems often require trained operators to monitor and control them, and human error can be a significant security risk. Some of the key human factors associated with SCADA systems include:
- Insufficient training, which can make it difficult for operators to respond effectively to security incidents
- Complacency, which can lead to lax security practices and make the system more vulnerable to cyber attacks
- Distractions, which can cause operators to miss critical alerts and fail to respond to security incidents in a timely manner
What are the three biggest security challenges end customers face in OT?

The three biggest security challenges end customers face in Operational Technology (OT) are cybersecurity threats, network vulnerabilities, and lack of visibility. These challenges can have significant consequences, including disruption of critical infrastructure, data breaches, and financial losses.
Understanding the Risks of OT Security
The security challenges in OT are complex and multifaceted. End customers face a range of risks, including phishing attacks, ransomware, and malware. To mitigate these risks, end customers must implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and incident response plans. Some key considerations for OT security include:
- Implementing segmentation to isolate critical systems and prevent lateral movement
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation efforts
- Developing incident response plans to quickly respond to and contain security incidents
Addressing the Lack of Visibility in OT Security
One of the biggest challenges in OT security is the lack of visibility into network activity and system performance. End customers often struggle to monitor and analyze network traffic, system logs, and security event data. To address this challenge, end customers can implement security information and event management (SIEM) systems, which provide real-time threat detection and incident response capabilities. Some key benefits of SIEM systems include:
- Improved threat detection and incident response capabilities
- Enhanced visibility into network activity and system performance
- Streamlined compliance reporting and regulatory requirements
Implementing Effective OT Security Measures
To implement effective OT security measures, end customers must take a proactive approach to security. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, implementing robust security controls, and providing ongoing training to personnel. End customers must also prioritize communication and collaboration between IT and OT teams to ensure a unified security posture. Some key considerations for implementing effective OT security measures include:
- Implementing robust access controls, such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access control
- Conducting regular security awareness training to educate personnel on security best practices
- Developing incident response plans to quickly respond to and contain security incidents
What is OT and SCADA?
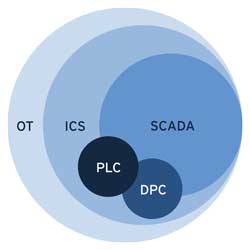
OT and SCADA are two critical systems used in various industries to monitor, control, and manage industrial processes. OT (Operational Technology) refers to the hardware and software used to control and monitor industrial equipment and processes, such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy production. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is a type of OT system that uses computers, networked data communications, and graphical user interfaces to monitor and control industrial processes. SCADA systems are used to collect data from sensors and other devices, analyze the data, and send control signals to devices to adjust the process as needed.
What is OT?
OT systems are used to control and monitor industrial equipment and processes, such as pumps, valves, and conveyors. These systems are designed to operate in real-time, meaning they can respond quickly to changes in the process. OT systems are typically used in industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and power generation. Some key features of OT systems include:
- Real-time control: OT systems can respond quickly to changes in the process, allowing for precise control and monitoring.
- Remote monitoring: OT systems can be accessed remotely, allowing operators to monitor and control the process from a central location.
- Automated control: OT systems can automate many control functions, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency.
What is SCADA?
SCADA systems are a type of OT system that uses computers and networked data communications to monitor and control industrial processes. SCADA systems are designed to collect data from sensors and other devices, analyze the data, and send control signals to devices to adjust the process as needed. SCADA systems are used in a variety of industries, including water treatment, transportation, and energy management. Some key features of SCADA systems include:
- Data collection: SCADA systems can collect data from a wide range of devices, including sensors, meters, and other monitoring equipment.
- Data analysis: SCADA systems can analyze data in real-time, allowing for quick identification of issues and optimization of the process.
- Control functions: SCADA systems can send control signals to devices to adjust the process, such as opening or closing valves or starting and stopping pumps.
Benefits of OT and SCADA
The use of OT and SCADA systems offers a number of benefits, including improved efficiency, increased productivity, and enhanced safety. By automating many control functions and providing real-time monitoring and control, OT and SCADA systems can help reduce the risk of human error and improve the overall reliability of industrial processes. Some other benefits of OT and SCADA systems include:
- Cost savings: OT and SCADA systems can help reduce energy consumption and improve resource allocation, leading to cost savings.
- Improved maintenance: OT and SCADA systems can provide real-time monitoring of equipment, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Regulatory compliance: OT and SCADA systems can help industries meet regulatory requirements by providing accurate and reliable data and control functions.
What are the unique security challenges within OT and industrial control systems?

The unique security challenges within Operational Technology (OT) and industrial control systems are distinct from those in traditional Information Technology (IT) environments. OT systems are designed to monitor, control, and manage industrial processes, such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy production. These systems often rely on legacy systems, proprietary protocols, and specialized hardware, which can make them more vulnerable to cyber threats.
Unique Challenges in OT and Industrial Control Systems
The OT environment presents several unique challenges, including the need to ensure reliability, availability, and safety of the systems. OT systems often have longer lifecycles than IT systems, which can make it difficult to implement security updates and patches. Additionally, OT systems may use custom-built software and hardware, which can make it challenging to find security solutions that are compatible with these systems. Some of the key challenges in OT and industrial control systems include:
- Interoperability: OT systems often consist of devices and systems from different manufacturers, which can make it difficult to ensure seamless communication and integration.
- Limited Resources: OT systems often have limited processing power, memory, and bandwidth, which can make it difficult to implement security measures that require significant resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: OT systems are subject to various regulations and standards, such as NERC CIP and IEC 62443, which can make it challenging to ensure compliance and auditing.
Threats to OT and Industrial Control Systems
OT and industrial control systems are vulnerable to a range of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks. These threats can be launched by nation-state actors, terrorist organizations, and cybercriminals, and can have devastating consequences, such as disruption of critical infrastructure and loss of life. Some of the key threats to OT and industrial control systems include:
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are sophisticated threats that use zero-day exploits and social engineering to gain unauthorized access to OT systems.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats are security risks that come from authorized personnel who have access to OT systems and may intentionally or unintentionally compromise the security of the system.
Security Measures for OT and Industrial Control Systems
To address the unique security challenges in OT and industrial control systems, several security measures can be implemented, including network segmentation, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Additionally, security protocols such as Secure Communication Protocols and Encryption can be used to protect data in transit and at rest. Some of the key security measures for OT and industrial control systems include:
- Conducting Regular Risk Assessments: Regular risk assessments can help identify vulnerabilities and prioritize security measures.
- Implementing Access Control: Access control measures, such as authentication and authorization, can help limit access to OT systems.
- Providing Security Training: Security training can help raise awareness and educate personnel on security best practices and procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is OT SCADA Security and Why is it Important?
OT SCADA security is a critical aspect of modern industrial operations, as it involves the protection of Operational Technology (OT) systems, such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, from cyber threats. These systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as power generation and transmission, water treatment, and transportation systems. The importance of OT SCADA security cannot be overstated, as a cyber attack on these systems could have devastating consequences, including the disruption of critical infrastructure, economic losses, and even loss of life. Therefore, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect OT SCADA systems from malicious actors and ensure the reliability and integrity of these systems.
What are the Challenges in Securing OT SCADA Systems?
Securing OT SCADA systems poses several unique challenges, including the use of legacy systems that are no longer supported by the manufacturer, the lack of standardization in OT protocols and devices, and the limited resources available for cybersecurity. Additionally, OT SCADA systems are often interconnected with other systems, making them vulnerable to cyber attacks that can propagate through the network. Furthermore, the convergence of OT and Information Technology (IT) systems has created new vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to implement comprehensive security solutions that take into account the specific needs and requirements of OT SCADA systems, including network segmentation, access control, and incident response planning.
How Can OT SCADA Systems be Protected from Cyber Threats?
Protecting OT SCADA systems from cyber threats requires a multi-layered approach that includes network security, endpoint security, and incident response planning. One of the most effective ways to protect OT SCADA systems is to implement network segmentation, which involves isolating critical systems and devices from the rest of the network. Additionally, access control measures, such as authentication and authorization, can be used to restrict access to OT SCADA systems and prevent unauthorized access. Furthermore, regular security updates and patches should be applied to OT SCADA systems to fix vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation by malicious actors. It is also essential to implement incident response planning, which involves developing a plan to respond to cyber attacks and minimize the impact of a security breach.
What are the Best Practices for Implementing OT SCADA Security Solutions?
Implementing OT SCADA security solutions requires a structured approach that takes into account the specific needs and requirements of the organization. One of the best practices for implementing OT SCADA security solutions is to conduct a thorough risk assessment, which involves identifying potential vulnerabilities and threats to the OT SCADA system. Additionally, security policies and procedures should be developed and implemented to ensure that all personnel understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining the security of the OT SCADA system. Furthermore, regular security training and awareness programs should be provided to personnel to ensure that they are aware of the latest threats and vulnerabilities and know how to respond to cyber attacks. It is also essential to continuously monitor the OT SCADA system for security breaches and incidents and to implement incident response planning to minimize the impact of a security breach.
Leave a Reply